What It Means for Our Climate Future
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Climate Change |
| Context |
| ● Global sea ice cover hit a new record low, with combined Arctic and Antarctic sea ice extent dropping to 15.76 million sq km between February 8-13, 2025. |
Analysis of the news:
Record Low in Global Sea Ice Cover
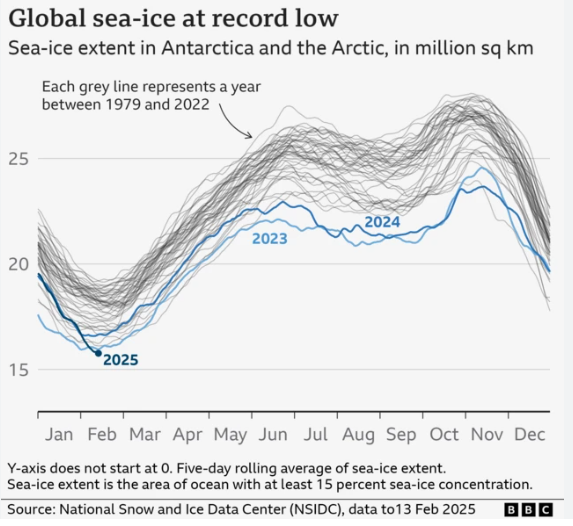
- This surpasses the previous record low of 15.93 million sq km observed in early 2023, as per data from the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
- Sea ice, distinct from icebergs and glaciers, plays a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by reflecting solar radiation and insulating ocean heat.
Current Trends in Sea Ice Decline
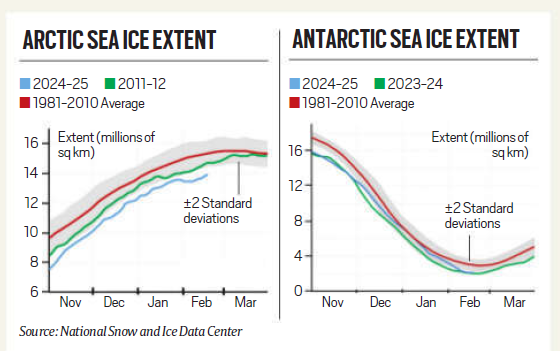
Arctic Sea Ice:
- Arctic sea ice has reached its lowest recorded extent for this time of year. Since the late 1970s, an average of 77,800 sq km of Arctic sea ice has been lost annually.
- Notably, between 1981 and 2010, Arctic sea ice shrank at a rate of 12.2% per decade each September, the month it typically reaches its minimum extent.
Antarctic Sea Ice:
- The Antarctic region, after witnessing year-on-year increases until 2015, experienced a dramatic loss of two million sq km of sea ice between 2014 and 2017.
- Although there was some recovery in 2018, sea ice levels again plummeted in 2023, falling two million sq km below average.
- Despite a slight improvement in 2024, levels remained 1.55 million sq km below the 1981-2010 average.
Key Drivers Behind the Dip
Arctic Factors:
- Delayed Freezing: Warm ocean waters around Hudson Bay delayed freezing.
- Storm Activity: Storms in the Barents and Bering Seas further fragmented fragile ice.
- Rising Temperatures: Elevated air temperatures, especially around Svalbard, exacerbated melting.
Antarctic Factors:
- Warm Air and Oceans: Higher air and sea temperatures during the southern hemisphere summer intensified ice melt.
- Ice-Breaking Winds: The thinner, more mobile Antarctic ice was vulnerable to winds that fragmented ice sheets.
- Ocean Warming: Persistent ocean warming provided a long-term backdrop for ice loss, affecting ice shelves and accelerating melt rates.
Implications of Declining Sea Ice
Accelerated Global Warming:
- Reduced sea ice exposes more ocean surface, increasing solar absorption and further warming the planet.
- Sea ice’s reflective surface (high albedo) is critical in maintaining cooler polar temperatures.
Polar Amplification:
- The polar regions are warming faster than the rest of the world.
- Loss of sea ice amplifies this effect, accelerating climate change impacts globally.
Disruption of Ocean Currents:
- Melting sea ice releases freshwater into oceans, reducing salinity and affecting the density-driven ocean circulation (thermohaline circulation).
- This slowdown can disrupt global climate patterns, threaten marine ecosystems, and destabilize polar ice shelves, raising the risk of further sea level rise.
Conclusion:
- The record-low sea ice extent serves as a stark warning of the accelerating impact of climate change.
- The intertwined dynamics of warming oceans, fragile ice systems, and disrupted global currents highlight the urgent need for global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the delicate balance of Earth’s polar ecosystems.
| Practice Question: Discuss the factors contributing to the recent record low in global sea ice cover and analyze its potential impact on global climate patterns and ocean circulation. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. On building resilient telecom infrastructure
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure |
| Context |
| ● Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) report assesses telecom network vulnerability to disasters and suggests measures for resilience and preparedness. |
Introduction to the Report
- The Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), launched in 2019, released a report assessing how well Indian telecom networks can withstand disasters.
- The report suggests ways for State governments to improve telecom network resilience during calamities.
Importance of Telecom Networks in Disasters
- Telecom networks play a crucial role in disaster response by enabling quick communication between authorities at different levels.
- Disruptions in telecom services can delay critical response efforts, putting lives and property at risk.
- These networks are vulnerable due to overhead cables, exposed towers, and dependency on electricity, all of which can be impacted by disasters like cyclones and earthquakes.
Impact of Disasters on Telecom Networks
- High-speed winds can damage towers, while overland cables can snap, leading to service disruptions.
- Coastal areas are especially vulnerable, as undersea cables connect India to the global internet. If these cables or landing stations are affected, there can be widespread network failures.
- Power failures during disasters are a major challenge, often being the primary reason for telecom outages.
Challenges in Restoring Telecom Services
- Severed undersea cables require specialized repair ships, leading to a slow restoration process.
- Restoring power to telecom towers and network centers is critical for maintaining connectivity during disasters.
- Telecom towers typically rely on backup batteries and fuel generators, but fuel shortages during disasters can affect their functionality.
- Real-time monitoring software helps authorities track network outages and allocate resources to restore services.
Recommendations for Strengthening Telecom Resilience
- Improving Power Infrastructure: Strengthening electricity supply to telecom networks can reduce disruptions.
- Building Stronger Towers: Cell towers, especially in coastal areas, should be designed to withstand high wind speeds.
- Enhancing Coordination: Better data collection and improved coordination between telecom operators and disaster management agencies can speed up restoration efforts.
- Dig-Once Policy: Encouraging simultaneous installation of underground utilities like water, gas, drainage, and fiber-optic cables reduces the risk of damage during infrastructure projects.
- Disaster Risk Modelling: Integrating disaster risk assessments into telecom infrastructure planning can improve preparedness.
- Parametric Insurance: Financial mechanisms like parametric insurance can help telecom operators recover faster from disasters and encourage better disaster-proofing of infrastructure.
Conclusion
- Small investments, such as installing backup generators at higher elevations to prevent flood damage, can significantly improve network resilience.
- Effective planning and proactive measures can ensure telecom networks remain functional during disasters, enabling better emergency response.
| Practice Question: How can India enhance the resilience of its telecom infrastructure to withstand natural disasters and ensure uninterrupted communication during emergencies? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. Did the iron age on Indian soil start from Tamil Nadu?
| Topic: GS1 – Indian History |
| Context |
| ● A recent report from Tamil Nadu suggests that the Iron Age in the region began around 5,300 years ago (4th millennium BCE).
● This challenges earlier studies that placed the beginning of the Iron Age in India much later. |
New Claims on the Beginning of the Iron Age
- The report states that when regions north of the Vindhyas were in the Copper Age, Tamil Nadu may have already transitioned to the Iron Age due to a lack of commercially usable copper ore.
| Earlier Research on the Use of Iron in India |
| ● The discovery of iron smelting was a significant step in human technological advancement.
● Previous research suggested that iron was introduced to India by migrants from the West. ● Earlier studies placed the beginning of iron use in India around 700-600 BCE. ● However, further research and radiocarbon dating indicated that iron smelting might have begun as early as the 16th century BCE. ● Excavations in Uttar Pradesh revealed evidence of iron artefacts, furnaces, and manufacturing between 1800 and 1000 BCE. ● The findings showed that large-scale iron production was present in the eastern Vindhyas and Central Ganga Plain by the early second millennium BCE. |
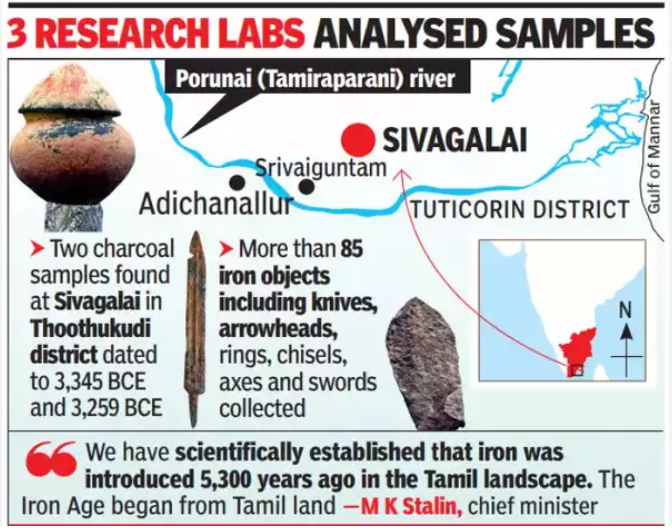
Excavations and Findings in Tamil Nadu
- Recent excavations in Tamil Nadu have uncovered iron artefacts dating back 4,200 years.
- A newly released report has further pushed back this timeline, placing the Iron Age in the region between 3,345 BCE and 2,953 BCE.
- Excavations have taken place at various sites, including Mayiladumparai, Sivagalai, Adichanallur, and Kilnamandi.
- These findings suggest that Tamil Nadu had a well-developed iron smelting and manufacturing culture much earlier than previously believed.
Implications of the Findings
- If these dates are accurate, Tamil Nadu might have entered the Iron Age before many other regions in India.
- The discoveries indicate that iron technology may have developed independently in southern India.
- The findings provide new insights into early technological advancements and social structures in the region.
- Scholars highlight that while the evidence suggests early iron use in Tamil Nadu, it does not confirm that the Iron Age originated there.
- These discoveries open new opportunities for research into Tamil Nadu’s ancient history and culture.
| Practice Question: Examine the recent discoveries on the antiquity of iron in Tamil Nadu, and their implications for understanding early technological advancements in India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
4. Theory and practice: the ethical core in Amartya Sen’s Weltanschauung
| Topic: GS3 – Economy |
| Context |
| ● Amartya Sen’s economic philosophy intertwines ethics and practice, emphasizing human welfare.
● His work on Social Choice Theory critiques utilitarianism and highlights inequality. |
Amartya Sen’s Approach to Economics
- Professor Bhabatosh Datta described Amartya Sen’s approach to economics as similar to that of Alfred Marshall, considering it a “handmaiden of ethics and a servant of practice.”
- When informed of this, Sen was deeply moved and expressed his gratitude towards his teacher.
Early Exposure to Social Realities
- From his teenage years at Patha Bhavan in Shantiniketan, Sen actively engaged with nearby Adivasi villages.
- He studied their daily lives, struggles, and deprivation firsthand.
- Sen used his bicycle for research on wages, prices, and gender-based nutritional deprivation, particularly during the Bengal Famine of 1943.
- This bicycle, a symbol of his early research, is now displayed in the Nobel Museum.
Ethics and Economics: A Deep Connection
- Sen believes that economics must be rooted in moral philosophy and practical applications, as envisioned by Adam Smith.
- He asserts that economics today must return to its foundational connection with human welfare and ethical dimensions.
The Development of Social Choice Theory
- Sen’s work on Social Choice Theory, which earned him the Nobel Prize in 1998, builds on a 200-year-old tradition from Bentham, Borda, and Condorcet.
- He acknowledges Kenneth Arrow’s contributions and the mathematical challenges posed by Arrow’s “impossible results.”
- Sen sought to address these challenges by expanding the framework beyond utilitarianism and voting theories.
- He believes that Social Choice Theory played a key role in shaping his understanding of the world.
Critique of Utilitarianism and Influence of Karl Marx
- Sen strongly critiques utilitarianism and instead values Karl Marx’s vision of freedom and ethics.
- He regards Marx as the most insightful economist on the transition “from necessity to freedom.”
- According to Sen, Marxian thought provides a clearer role for freedom than any other standard moral philosophical system.
Influence of Kant and Classical Literature
- Sen deeply admires Immanuel Kant for integrating ethics with reason in philosophy.
- He advises reading Kant’s The Moral Law and Critique of Pure Reason for a deeper understanding of ethical reasoning.
- He also draws inspiration from the Sanskrit play Mudrarakshasa, where the protagonist prioritizes nyaya (ethical justice) over niti (fixed rules).
The Core Problem: Inequality
- Sen believes that all global issues originate from some form of inequality.
- He argues that ethical principles must guide practical solutions to these inequalities.
Global Recognition and Legacy
- Nadine Gordimer praised Sen as one of the few great intellectuals who can provide clarity in an era of complexity and conflict.
- His commitment to ethics and justice continues to shape modern economic and social thought.
| Practice Question: Discuss how Amartya Sen’s integration of ethics and economics challenges traditional utilitarian perspectives and contributes to addressing inequality in modern societies. (250 Words /15 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Prime Minister pays homage to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj on his Jayanti
| Topic: GS1 – History – Personalities |
| Context |
| ● PM Modi honors Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj on his Jayanti, 19th February, highlighting his legacy of courage and Swarajya. |

Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj:
Early Life and Background
- Born on 19th February 1630 at Shivneri Fort, Maharashtra.
- Son of Shahaji Bhosale, a general in the Deccan Sultanates, and Jijabai, a deeply religious and strong-willed mother.
- Grew up learning administration, warfare, and statecraft under the guidance of his mother and mentor, Dadaji Kondadev.
Establishment of Swarajya
- Laid the foundation of Hindavi Swarajya (self-rule) against the Mughal and Sultanate rule.
- Captured Torna Fort in 1646, marking the beginning of his conquests.
- Adopted guerrilla warfare tactics, using the terrain of the Western Ghats to his advantage.
Military Prowess and Naval Strength
- Built a strong Maratha navy, establishing naval bases at Sindhudurg and Vijaydurg to protect against foreign invasions.
- Successfully defended his kingdom against Aurangzeb’s Mughals, the Adilshahi of Bijapur, and foreign invaders.
- Fought and won several key battles, including the Battle of Pratapgad (1659) against Afzal Khan.
Coronation and Administration
- Crowned as Chhatrapati on 6th June 1674 at Raigad Fort.
- Established a well-organized administrative system with Ashta Pradhan (Council of Eight Ministers).
- Introduced progressive tax policies and ensured welfare-oriented governance.
Religious Tolerance and Social Reforms
- Promoted secular governance, respecting all religions and ensuring protection of places of worship.
- Opposed caste discrimination and empowered lower castes to serve in the military.
Legacy and Influence
- Passed away on 3rd April 1680, leaving behind a vast and strong Maratha Empire.
- His ideals of Swarajya, good governance, and military strategy continue to inspire generations.
- Revered as a symbol of valor, patriotism, and just rule in India.
| Practice Question: How did Shivaji Maharaj’s naval strategy influence later Indian military tactics? (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. India and Argentina Strengthen Cooperation in Lithium Exploration and Mining with a MoU
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Bilateral Relations |
| Context |
| ● A high-level meeting was held between representatives from India and Argentina to enhance cooperation in the mining sector, focusing on lithium exploration and investments. |
India-Argentina Cooperation in Lithium Exploration
- A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between an Indian PSU under the Ministry of Mines and the Provincial Government of Catamarca, Argentina.
- Argentina, part of the ‘Lithium Triangle,’ holds significant lithium reserves crucial for electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy storage.
- Indian companies are already involved in lithium exploration projects in Catamarca, with efforts underway to expand participation.
- Both sides discussed investment opportunities, long-term supply agreements, and joint ventures to strengthen India’s access to critical minerals.
- Talks included policy frameworks, regulatory aspects, and sustainable mining practices to ensure responsible resource development.
- The agreement is expected to accelerate lithium exploration projects and improve resource security for India.
| Importance of Lithium for Modern Economies: |
| ● Essential for Batteries: Used in lithium-ion batteries, powering electric vehicles (EVs), smartphones, laptops, and renewable energy storage systems.
● Key to Green Energy Transition: Supports solar and wind energy storage, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. ● Electric Vehicle Industry: Critical for EV batteries, driving the shift toward sustainable transportation. ● Lightweight and High Energy Density: Offers superior energy storage capacity, improving efficiency in portable devices. ● Strategic Resource: Countries are securing lithium supply chains for economic and energy security. ● Industrial and Medical Uses: Used in aerospace alloys, ceramics, glass manufacturing, and mental health treatments. |
| Practice Question: Why Is Lithium Important? How does India plan to secure a stable lithium supply amid rising global demand? (250 Words /15 marks) |
3. India elected to Vice Presidency of International Organization of Aids to Marine Navigation (IALA)
| Topic: GS2 – International Relations – Important International institutions |
| Context |
| ● India has been elected as the Vice President of the International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA) during the meeting held in Singapore. |
Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA):
- Established in 1957, IALA is an intergovernmental organization focused on marine navigation safety.
- IALA transitioned into an intergovernmental organization (IGO) on August 22, 2024.
- It sets global standards for Aids to Navigation (AtoN), including lighthouses, buoys, and electronic systems.
- The organization promotes harmonization of navigation practices to ensure safe and efficient maritime transport.
- IALA works with coastal nations, maritime authorities, and industry stakeholders to improve navigation safety.
- It supports new technologies, such as e-Navigation and digital aids.
- IALA provides training, technical guidelines, and capacity-building programs for member states.
4. World Day of Social Justice – 20th February
| Topic: GS2 – Social Justice |
| Context |
| ● World Day of Social Justice, observed on February 20th, promotes global efforts to address poverty, exclusion, unemployment, and equality. |
Introduction
- World Day of Social Justice is observed on February 20th by the United Nations to address poverty, exclusion, and unemployment and promote equality and solidarity.
- India’s Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) works towards bridging socio-economic gaps through legislation, grassroots initiatives, and global partnerships.
Background & Global Context
- The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) established this day in 2007, with annual observances since 2009.
- The focus is on social development, justice, and peace.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) adopted the Declaration on Social Justice for a Fair Globalization (2008), emphasizing Decent Work Agenda.
- The Social Protection Floor (2009) initiative by the United Nations ensures basic social guarantees for all.
Social Justice in India
- The Indian Constitution upholds social justice through various rights and policies.
- Key constitutional provisions include:
- Preamble: Ensures justice, equality, and dignity.
- Fundamental Rights: Prohibits human trafficking (Article 23) and child labor (Article 24).
- Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP): Promote equality, fair wages, and legal aid.
- The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJE), established in 1998, promotes inclusive growth for marginalized groups.
Government Initiatives for Social Justice
- PM-AJAY (2021-22): Uplifts Scheduled Castes (SCs) through skill development, income generation, and infrastructure support.
- SRESHTA: Supports SC students by funding high-quality residential schools.
- Purple Fests: Events promoting inclusion and accessibility for persons with disabilities.
- NAMASTE (2023-24): Ensures dignity and safety for sanitation workers in urban areas.
- SMILE: Aims for a begging-free India, rehabilitating transgender persons and individuals engaged in begging.
- PM-DAKSH (2021-26): Provides free skill training to marginalized groups for employment opportunities.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (2020): Targets 272 high-risk districts to combat substance abuse.
Conclusion
- The World Day of Social Justice highlights the importance of equity and inclusion.
- Increased budget allocations and inclusive platforms reaffirm India’s commitment to justice and equal opportunities for all.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the World Day of Social Justice. What challenges hinder the full implementation of these social justice initiatives in India? (150 Words /10 marks) |
If you like thus Daily Current Affiars Don’t forget to check previous one –Breaking Russia and U.S. Strike Landmark Deal to End Ukraine War
