| Topic: GS2 – Governance |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:

Top Performers and Improvements
- The 2024 Panchayat Devolution Index (PDI), developed by the Indian Institute of Public Administration (IIPA), highlights Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu as the top performers in devolution of powers to panchayats.
- Uttar Pradesh and Bihar recorded the most significant improvements.
- The index, based on six parameters—framework, functions, finances, functionaries, capacity building, and accountability—shows a modest national average increase from 92 (2013-14) to 43.89 (2024).
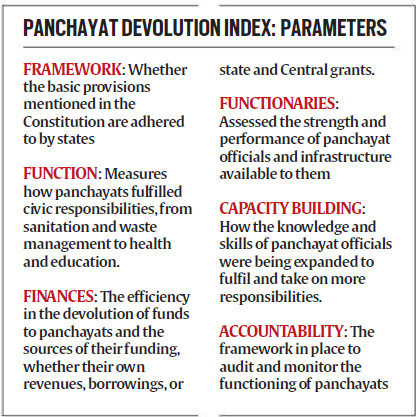
- However, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh, and Jharkhand rank lowest, with Manipur, Arunachal, and Haryana showing the biggest declines.
Representation and Inclusivity Challenges
- The representation of marginalized groups remains uneven.
- While Odisha leads with 51% women representation, Uttar Pradesh trails at 33.33% due to a lower reservation threshold.
- The national average for women representatives rose marginally to 44% in 2024. For marginalized communities, Punjab leads in SC representation (36.34%), Chhattisgarh in ST representation (41.04%), and Bihar in OBC representation (39.02%).
- However, disparities persist, with some states lagging in meeting reservation thresholds.
Infrastructure and Funding Constraints
- Inadequate infrastructure and inconsistent funding continue to hinder panchayats.
- Of the ₹47,018 crore allocated by states in 2023-24, only ₹10,761 crore was released by November 2023.
- Infrastructure gaps are stark, with only seven states and UTs reporting 100% pucca panchayat buildings, while Arunachal Pradesh (5%) and Odisha (12%) lag significantly.
- Digital connectivity also remains a challenge—while 14 states and UTs reported 100% internet access, Haryana reported zero and Arunachal just 1% internet access in panchayats.
Way Forward
For strengthening local governance, states must ensure:
- Timely fund releases and consistent financial support.
- Universal digital infrastructure and internet connectivity in panchayats.
- Enhanced capacity building and training programs for local representatives.
- Strict adherence to reservation policies for better gender and social inclusivity.
A balanced devolution of powers, coupled with adequate infrastructure and inclusive representation, is essential for empowering panchayats and realizing the vision of grassroots democracy in India.
| Practice Question: Despite constitutional provisions for decentralization, Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in India continue to face challenges related to devolution of powers, representation, and infrastructure. Critically examine these challenges in light of the 2024 Panchayat Devolution Index and suggest measures to strengthen grassroots governance. (150 Words /10 marks) |
2. Global Glacier Melting Triggers 2 cm Sea Level Rise, Posing Severe Coastal Flood Risks
| Topic: GS3 – Environment – Climate Change |
| Context |
|
Analysis of the news:
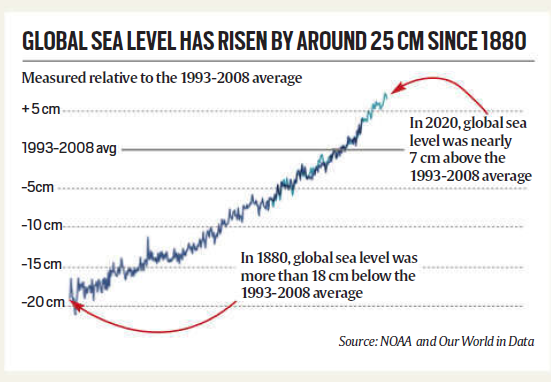
Extent of Glacier Melting and Sea Level Rise
- Glaciers have been losing an alarming 273 billion tonnes of ice annually for the last 25 years.
- While 2 cm might seem negligible, experts warn that each centimetre of sea-level rise exposes an additional 2 million people to annual flooding, emphasizing the severe human impact.
Key Drivers of Sea Level Rise
1. Glacier and Ice Sheet Melting
- Global warming has accelerated the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, with glaciers losing between 2% and 39% of their ice regionally and 5% globally since 2000.
- This loss surpasses that of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets by 18%, posing a critical threat to coastal populations.
2. Thermal Expansion of Seawater
- As ocean temperatures rise, seawater expands—a phenomenon known as thermal expansion—responsible for one-third to half of the global sea level rise, according to NASA.
- This thermal expansion, coupled with ice melt, exacerbates sea level increases.
Sea Level Rise Trends and Regional Variations
- Since 1880, global sea levels have risen by 21 cm, with a sharp acceleration noted in recent decades—from 18 cm per year (1993) to 0.42 cm per year (2024).
- The rise is uneven globally; for example, the southwestern Indian Ocean sees a rise of 5 mm per year, surpassing the global average.
- In India, coastal cities like Mumbai have experienced the highest sea level rise (44 cm between 1987 and 2021), making them highly vulnerable due to low elevation.
- Other affected cities include Haldia (2.726 cm), Visakhapatnam (2.381 cm), and Kochi (2.213 cm).
Why Rising Sea Levels Are Concerning
1. Increased Flooding and Coastal Erosion
- Rising seas result in frequent coastal flooding, intensifying coastal erosion and displacing coastal populations.
- For example, the West Bengal coast lost 99 sq km of land between 1990 and 2016, highlighting the dire consequences of unchecked sea level rise.
2. Threat to Coastal Ecosystems and Freshwater Supplies
- Storm surges become more intense with higher sea levels, affecting mangroves, coral reefs, and salt marshes.
- Additionally, saltwater intrusion threatens freshwater reserves, impacting agriculture and daily water consumption.
3. Population Vulnerability
- Approximately 29% of the global population lives within 50 km of the coast, and 15% within 10 km, making large populations vulnerable to flooding, displacement, and economic disruption.
The Way Forward:
If greenhouse gas emissions continue unchecked, NASA estimates an additional 20 cm rise in sea levels by 2050, potentially doubling flood frequencies globally. Addressing this crisis requires:
- Global emission reductions to slow glacier melting.
- Coastal resilience planning in vulnerable regions.
- International cooperation to mitigate displacement and economic loss.
Conclusion
- The accelerating rise in sea levels, driven by glacier melting and thermal expansion, poses a serious threat to coastal communities, ecosystems, and global economies.
- With cities like Mumbai already witnessing significant impacts, immediate climate action is critical to prevent further disasters and ensure a sustainable future.
| Practice Question: Discuss the major causes of global sea level rise and analyze its potential socio-economic and environmental impacts, with a special focus on vulnerable coastal regions in India. (150 Words /10 marks) |
3. Union Health Ministry takes immediate action in response to concerns on export of unapproved drug combination of Tapentadol and Carisoprodol
| Topic: GS2 – Social justice – Health |
| Context |
|
About Tapentadol and Carisoprodol:
- Tapentadol: It is an opioid analgesic used for treating moderate to severe pain.
- It works by binding to opioid receptors and inhibiting norepinephrine reuptake, providing dual-action pain relief.
- It is available in immediate-release (50, 75, and 100 mg) and extended-release (100, 150, and 200 mg) tablet forms.
- Carisoprodol: It is a centrally acting muscle relaxant used to relieve musculoskeletal pain and discomfort.
- It acts on the brain and spinal cord to suppress nerve signals causing pain.
- The combination of Tapentadol and Carisoprodol is not approved in India due to safety concerns.
Why has the government banned the export?
- Aveo Pharmaceuticals exported these drugs without proper authorization, violating regulatory norms.
- A CDSCO audit revealed non-compliance, leading to a stop activity order and seizure of 1.3 crore tablets.
- The ban ensures public safety, prevents misuse, and upholds pharmaceutical industry standards.
4. First detailed map of moon’s south pole made from Chandrayaan data
| Topic: GS3 – Science and Technology |
| Context |
| Scientists have created the first detailed geological map of the moon’s south polar region.The new map is expected to provide valuable insights into the moon’s origin and evolution. |
Confirmation of Lunar Magma
- Data from the Pragyan rover confirmed that the moon has an underground ocean of molten rock, also known as primordial magma.
- Previous missions had suggested the presence of magma beneath the moon’s surface, but their landing sites were near the equator and mid-latitude regions, far from the poles.
- Chandrayaan-3’s landing in a high-latitude region provided critical evidence that the ancient ocean of molten lava extended across the entire moon.
Geological Insights from the Map
- The geological map reveals an undulating landscape with highlands and low, flat plains.
- Scientists identified Schomberger crater as the primary source of debris covering the landing zone.
- By analyzing the crater formations, they estimated the region’s age to be about 3.7 billion years.
Earth-Moon Connection
- The moon and earth have similar evolutionary histories.
- Scientists believe that around 4.5 billion years ago, a massive planetary rock collided with the young earth, leading to the formation of the moon.
- The geochemical similarities between the earth and moon further support this theory.
Importance of Lunar Craters
- The South Pole-Aitken Basin, one of the oldest and largest craters in the Solar System, is near the Vikram lander’s touchdown site.
- Lunar craters help scientists study impact craters on earth and other inner planets.
- Since the moon has no atmosphere, its craters remain well-preserved for millions of years.
Concerns About Lunar Exploration
- Since 1959, multiple missions have left debris on the moon’s surface, leading to concerns about environmental contamination.
- Scientists worry that landers, rovers, and human activities may disturb the regolith and alter the moon’s exosphere.
- Exhaust fumes from lunar landers could contaminate lunar ice, affecting research on water reserves.
- As lunar colonization and resource mining increase, these issues may become more significant.
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of Chandrayaan-3’s findings in understanding the moon’s geological history and its implications for future lunar exploration. (150 Words /10 marks) |
5. Why VOC port needs an outer harbour
| Topic: GS3 – Indian Economy – Infrastructure |
| Context |
| The ₹7,056-crore outer harbour project at VOC port in Thoothukudi is being revived after facing delays for over 20 years. |

Need for an Outer Harbour
- The size of container ships has increased significantly, with some extending over 400 meters and carrying 22,000 TEUs.
- VOC port can currently handle only half this capacity, making an outer harbour necessary for handling larger vessels.
- Modernizing the inner harbour alone is not sufficient to meet future demand.
Alignment with the Sagarmala Scheme
- The outer harbour will allow VOC port to handle 14,000-TEU Neo Panamax and other large vessels.
- This will help VOC port leverage its proximity to international sea routes and become a key trade hub.
- By 2044, container traffic at the port is expected to grow to 2.8-4.3 million TEUs from 0.74 million TEUs in 2023-24.
Delays and Infrastructure Challenges
- The inner harbour’s draught is being increased from 14.2 m to 15.5 m to accommodate larger ships.
- Plans for a new transshipment port at Kanyakumari have been delayed due to multiple factors.
- The lack of a backup area in the inner harbour limits its potential as a container yard.
Potential Impact of the Sri Lanka Crisis
- The economic crisis in Sri Lanka has affected port operations in Colombo, creating an opportunity for VOC port.
- If developed on time, VOC port could attract more mainline vessels and transshipment business.
- The second phase of the outer harbour project will enable handling vessels requiring an 18-m draught.
Reducing Transshipment Costs
- 65% of containers from Thoothukudi are currently transshipped at Colombo.
- Exporters and importers pay $150 per TEU and face a week-long transit delay due to this dependency.
- Developing VOC port as an alternative to Colombo will reduce costs and save foreign exchange.
Industrial Growth and Future Prospects
- Several industries, including solar manufacturing, vehicle production, and space technology, have emerged near the port.
- The increase in cargo volume from these industries highlights the need for port expansion.
- The outer harbour project has faced multiple delays since its approval in 2005, resulting in lost economic opportunities.
| V. O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port |
|
| Practice Question: Discuss the significance of the V.O. Chidambaranar (VOC) Port in India’s maritime trade and its potential as a transshipment hub. What challenges does the port face in handling larger vessels, and how can infrastructure development address these challenges? (150 Words /10 marks) |
Prelims Facts
1. Condensed matter: a big piece of physics
| Context |
|
What is condensed matter physics?
- Definition: Condensed matter physics is the study of solid and liquid matter and how their particles interact.
- Focus: It examines how large groups of particles behave when they strongly interact with each other.
- Comparison with Gases: Unlike gases, where interactions are weak, condensed matter deals with strong interactions.
- Subcategories:
- Electronic Condensed Matter – Studies how electrons move in solids and liquids, including semiconductors.
- Magnetic Condensed Matter – Explores different types of magnets and magnetism.
- Soft Matter Physics – Studies materials that are easily deformed but not broken, like biological tissues.
- Nanoscience – Examines tiny objects that show both classical and quantum properties.
- Superfluidity – Studies materials that flow without resistance, like superconductors.
- Technological Impact: Research has led to modern computing, lasers, optical fibers, and new materials.
- Quantum Condensed Matter: Focuses on quantum physics effects to develop advanced electronics and quantum computers.
2. Hub in the making: Vizhinjam port vies for global stature
| Context |
|
Key Features of Vizhinjam Port
- The port has a natural depth of 18-20 meters, making it suitable for large mother vessels.
- It is strategically located near international shipping routes, improving transshipment efficiency.
- Since July 2024, 144 ships and 2.9 lakh containers have been handled.
Development of a Special Economic Zone (SEZ)
- Plans are in place to develop a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) similar to one at another major Indian port.
- The SEZ will include logistics hubs, warehouses, and industrial clusters to boost trade.
- Strong connectivity with the airport and Kerala’s spice and seafood industries will help attract global businesses.
Expansion into a Sea-Air Transshipment Hub
- The port will link key global trade routes between Shanghai, Busan, Rotterdam, and major Indian ports.
- A new cargo terminal is being built at Trivandrum International Airport for better export capabilities.
- The ₹1,300 crore investment in the airport terminal will improve the handling of 2,500 tonnes of cargo.
Infrastructure Developments
- The port’s handling capacity will grow to 4.5 million TEUs by 2028.
- A 10-km rail tunnel will connect the port to inland transport within four years.
- Road connectivity to National Highway 66 will be ready in two years.
Future Growth and Economic Impact
- The expansion supports Kerala’s focus on 22 priority industries, including defence, space manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals.
- In the second phase, Vizhinjam will double connectivity routes and expand its cargo handling capabilities.
- The port aims to handle one million TEUs in its first year, setting a new record for Indian ports.
3. HIV Self-Testing Empowers Youth in Mizoram, Boosts First-Time Testing Rates
| Context |
|

Analysis of the news:
HIV Burden in Mizoram
- Mizoram has the highest HIV prevalence in India, with 2.73% of adults infected — 13 times the national average.
- High-risk groups such as injecting drug users (19.8%) and female sex workers (24.7%) exhibit the highest infection rates.
- The epidemic is primarily driven by drug-related practices and commercial sex work.
Role and Impact of HIV Self-Testing
- HIV Self-Testing (HIVST): Individuals collect and interpret their own test results using blood and saliva samples.
- Globally adopted in 41 countries since WHO’s 2016 guidelines, India has yet to introduce formal regulations.
- The Mizoram study engaged community influencers, religious leaders, and youth associations for effective outreach.
Key Findings of the Study
- Over six months, 2,101 youths in Aizawl took HIV self-tests, with 84% being first-time testers.
- Among those testing positive, 85% underwent confirmatory tests and were linked to antiretroviral therapy (ART).
- The initiative outperformed traditional awareness campaigns by ensuring early detection and treatment.
4. Microsoft Unveils Majorana 1 Quantum Chip
| Context |
| Microsoft has unveiled Majorana 1, a groundbreaking quantum chip designed to produce more reliable and scalable qubits. Regarded as a significant leap toward practical quantum computing, Majorana 1 aims for commercial deployment between 2027 and 2029. |
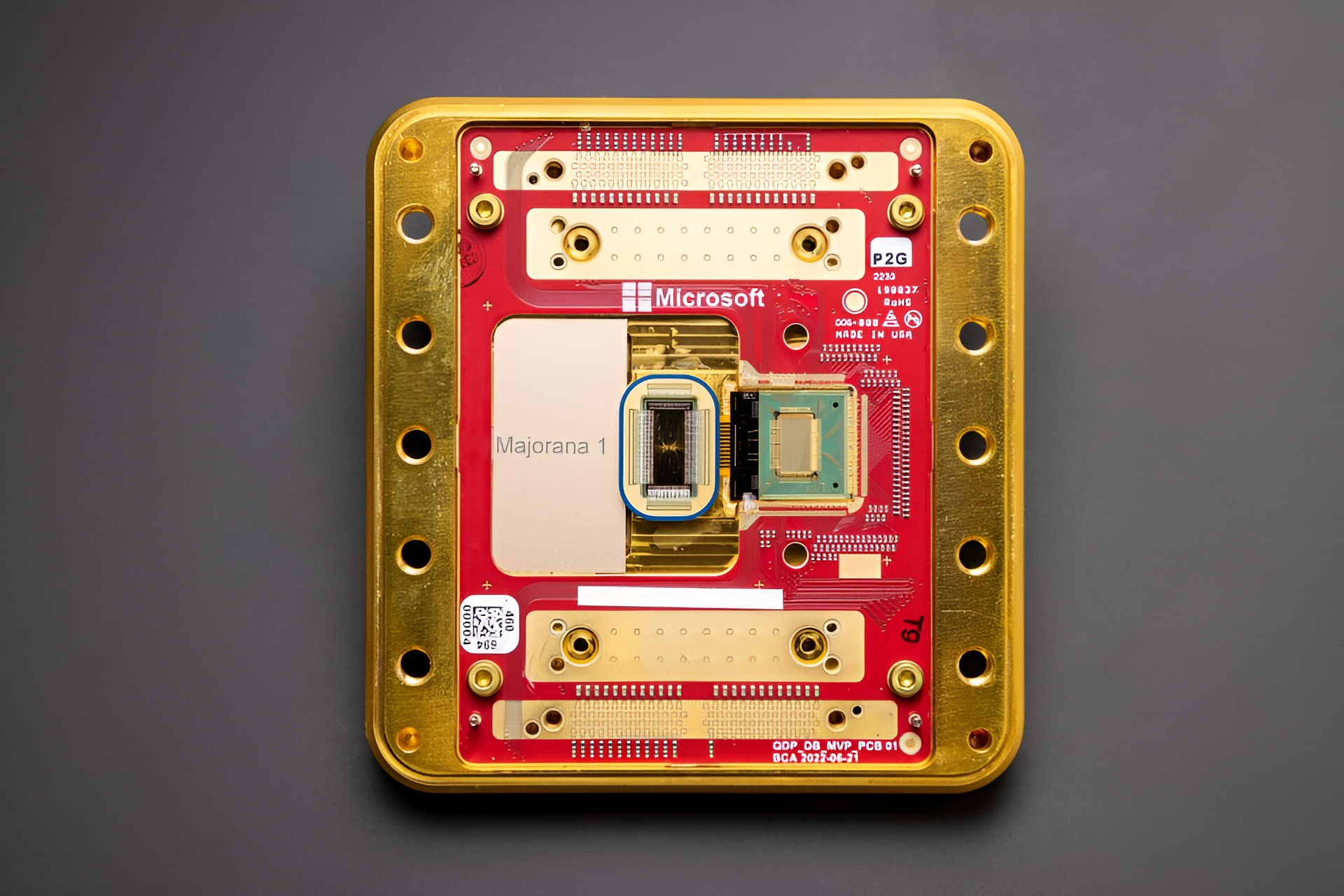
Analysis of the news:
Majorana Particles
- The core innovation lies in the engineering of Majorana quasiparticles using topological conductors.
- These particles enable qubits in a topological state, distinct from conventional states of matter.
- Topoconductors, made by combining indium arsenide and aluminum, form the basis of these stable qubits, potentially reducing error rates significantly.
Key Features of Majorana 1
- Architecture: An eight-qubit chip based on the Topological Core architecture, scalable to a million qubits.
- Material Composition: Indium arsenide (semiconductor) paired with aluminum (superconductor).
- Potential Impact: Capable of addressing complex challenges like breaking down microplastics and developing self-healing materials.
Comparisons with Rivals
- Despite Majorana 1 having only eight qubits, its scalable architecture contrasts with Google’s Willow (106 qubits) and IBM’s R2 Heron (156 qubits).
- Microsoft emphasizes quality and scalability over raw qubit count, claiming long-term advantages in error correction and system stability.
Quantum vs. Classical vs. Supercomputers
- Classical Computers: Use binary bits (0 or 1).
- Supercomputers: Employ accelerated classical architectures but remain bound by classical computing principles.
- Quantum Computers: Utilize qubits capable of existing in multiple states simultaneously, enabling faster and more complex computations. Quantum gates, unlike classical logic gates, process qubits in reversible operations.
Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum systems could revolutionize industries by:
- Mapping molecular behavior for self-healing materials.
- Solving advanced chemistry problems related to corrosion and material strength.
- Accelerating AI development through quantum-generated synthetic data.
If you like this Daily Current Affairs Don’t forget to check this –Why Government Spending in India is More Important Than You Think
